How to install the Proton Vpn on Linux
Debian-based distros
Our app currently supports Linux Debian 10+, Ubuntu 18.04+, and most distros based on these Linux versions (including Mint and Kali, but not Ubuntu Server or Raspbian).
If you are using an older version of our Linux client, we recommend that you uninstall it before installing the new app. Please see the Notes(1) section at the end of this article for instructions.
Open Terminal and enter the following commands (or just copy and paste them in). Note: before starting, we recommend running the following command to ensure you system is up to date:
sudo apt-get upgrade
1. Add the ProtonVPN repository to your system’s software sources(2):
wget -q -O - https://repo.protonvpn.com/debian/public_key.asc | sudo apt-key add - Followed by:
sudo add-apt-repository 'deb https://repo.protonvpn.com/debian unstable main'Note: Once this repo has been added, the app will be kept updated by your default package manager.
2. Install the client:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install protonvpnFedora 33
Please note that our app does not work in earlier versions of Fedora. To upgrade your system, run:
dnf upgrade1. Add the ProtonVPN repository to your system’s software sources.
To do this, create a text file in your /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory using a text editor such as Nano or Vim:
sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-33-unstable.repoor
sudo vim /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora-33-unstable.repoCopy and paste the following text into the new file:
[proton-fedora-33-unstable] name="fedora-33-unstable" baseurl=https://repo.protonvpn.com/fedora-33-unstable/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://repo.protonvpn.com/fedora-33-unstable/public_key.asc
Save and exit the newly created file using Ctrl + O, followed by Ctrl + X in Nano, or pressing the Esc button and typing “:x” <enter> in Vim.
2. Install the client:
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf install protonvpnHow to use the official Linux beta app
1. Log in using your regular Proton/ProtonVPN account details using the following command (please note that these are not the OpenVPN/IKEv2 login credentials used by the older community Linux client).
protonvpn-cli login [ProtonVPN username]
You will be prompted to enter your password. If you don’t have a ProtonVPN account you can sign up for one here.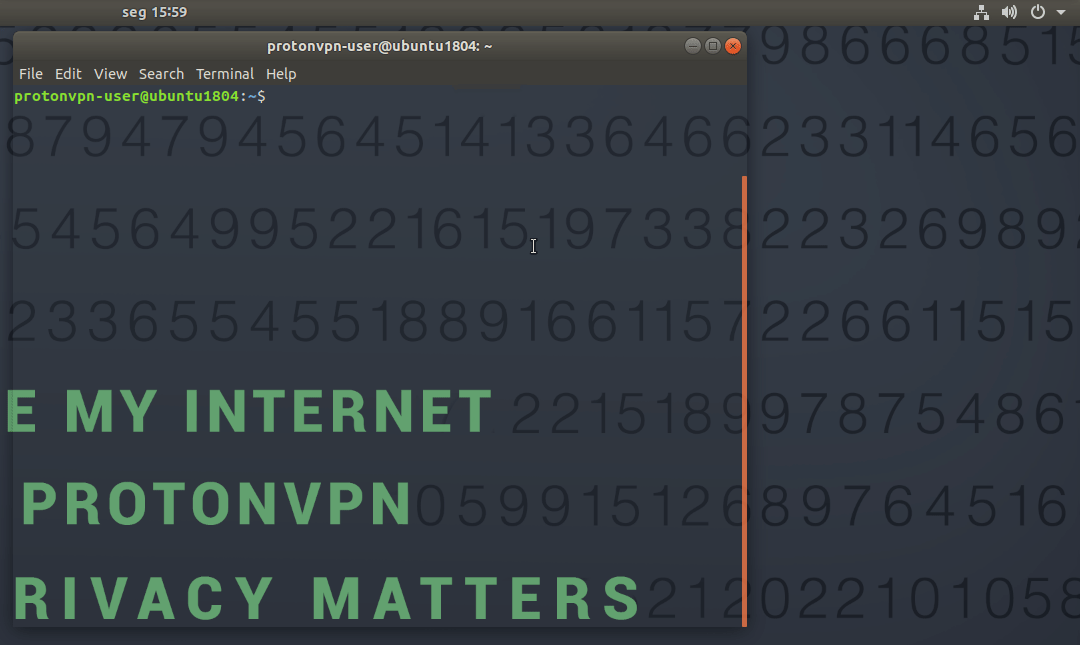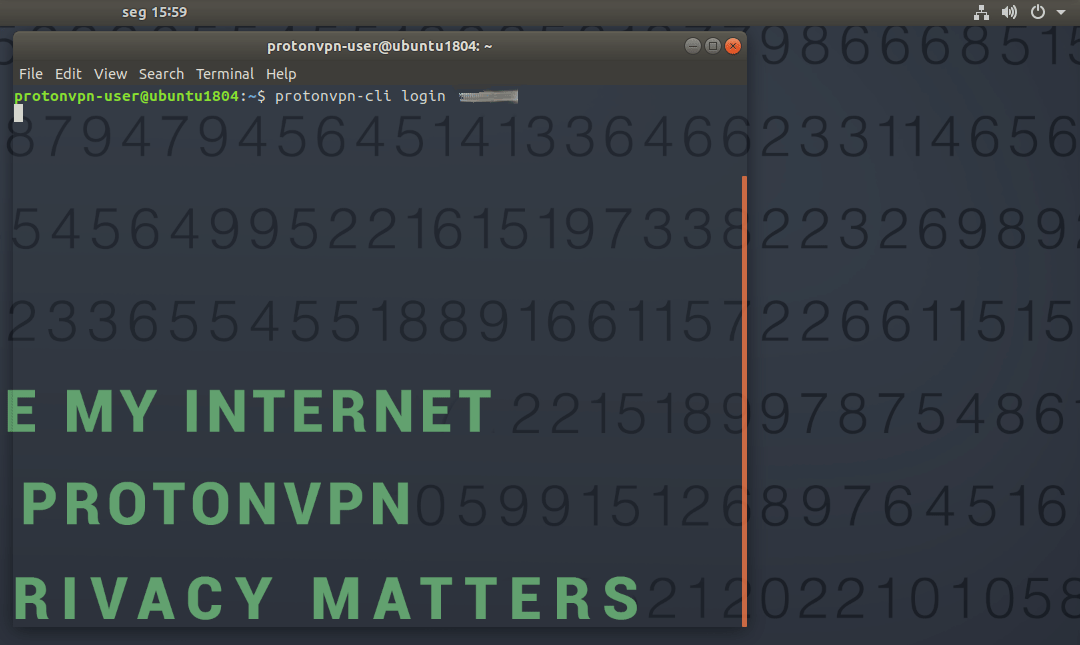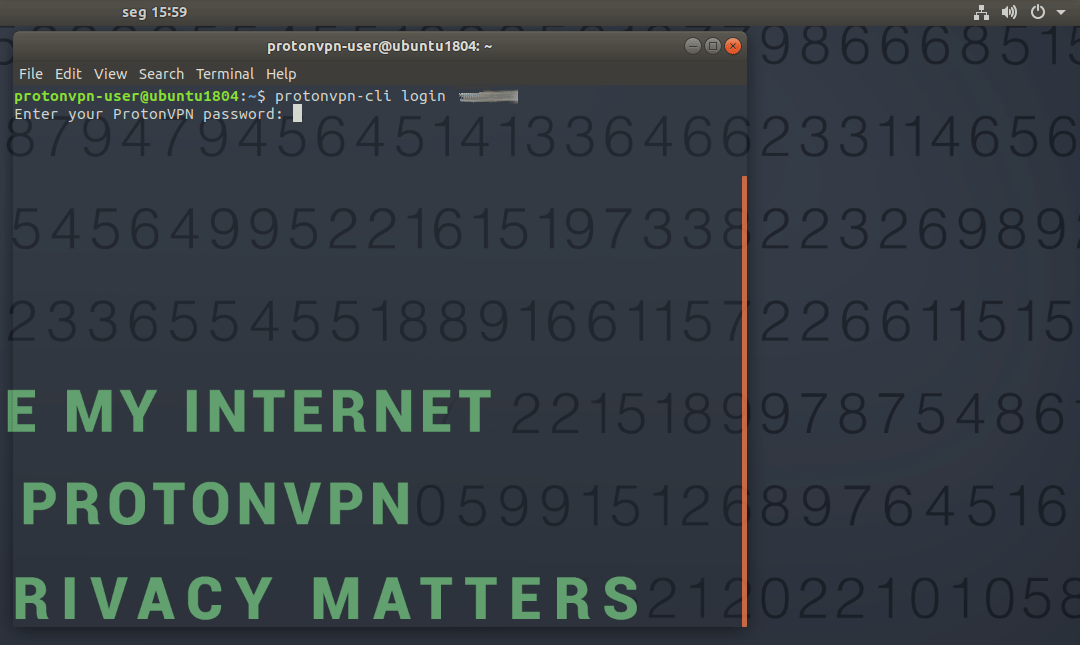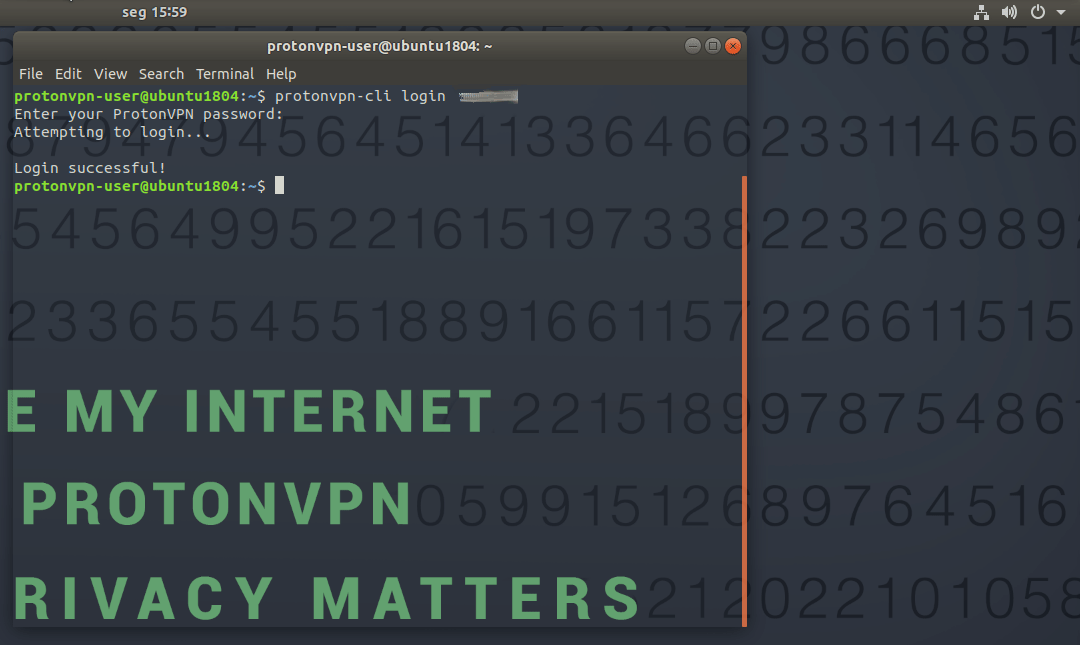 The app will remember your login details between sessions. 2. Open a list of ProtonVPN servers with:
The app will remember your login details between sessions. 2. Open a list of ProtonVPN servers with:
protonvpn-cli connect (or protonvpn-cli c)
3. Select a server location and click OK.Select a server at that server location and click OK. 4. Select udp or tcp (we recommend udp unless you have a reason to choose tcp).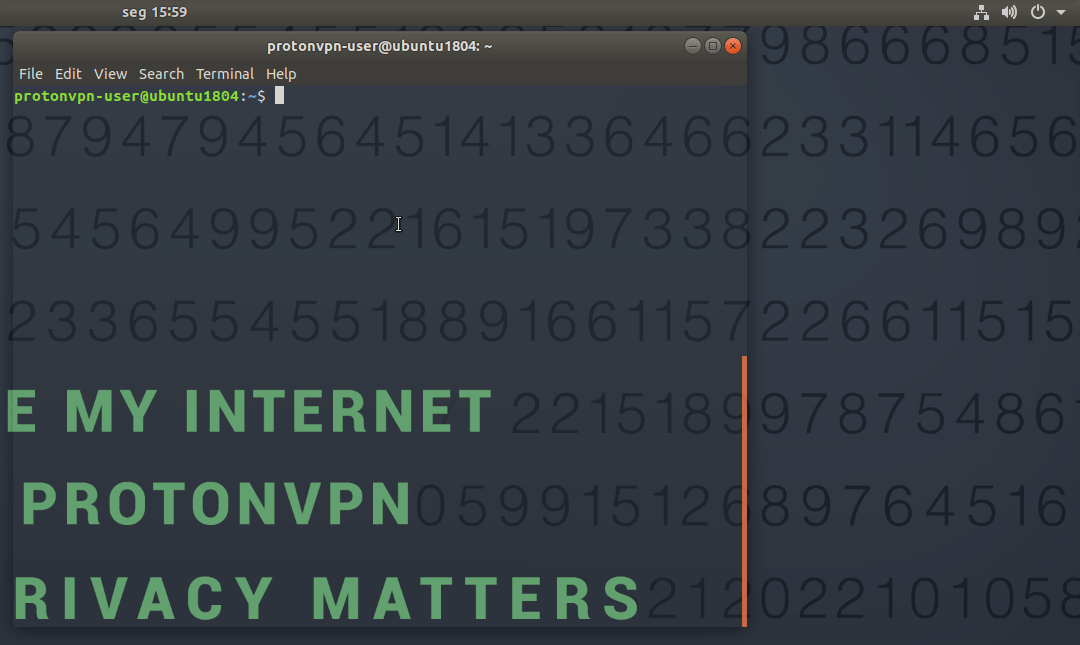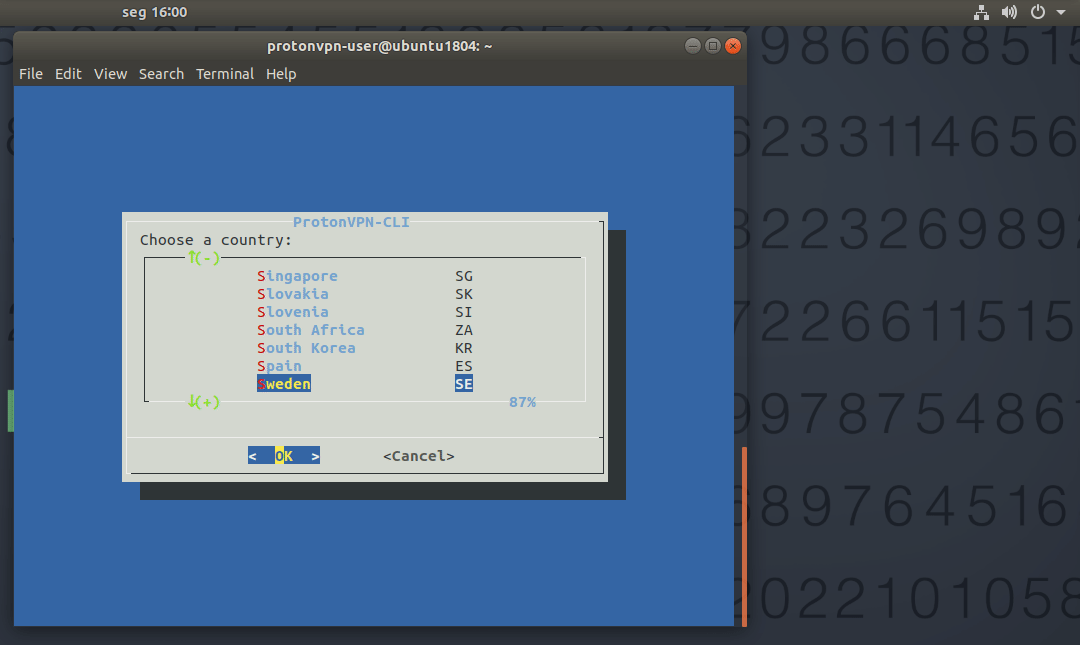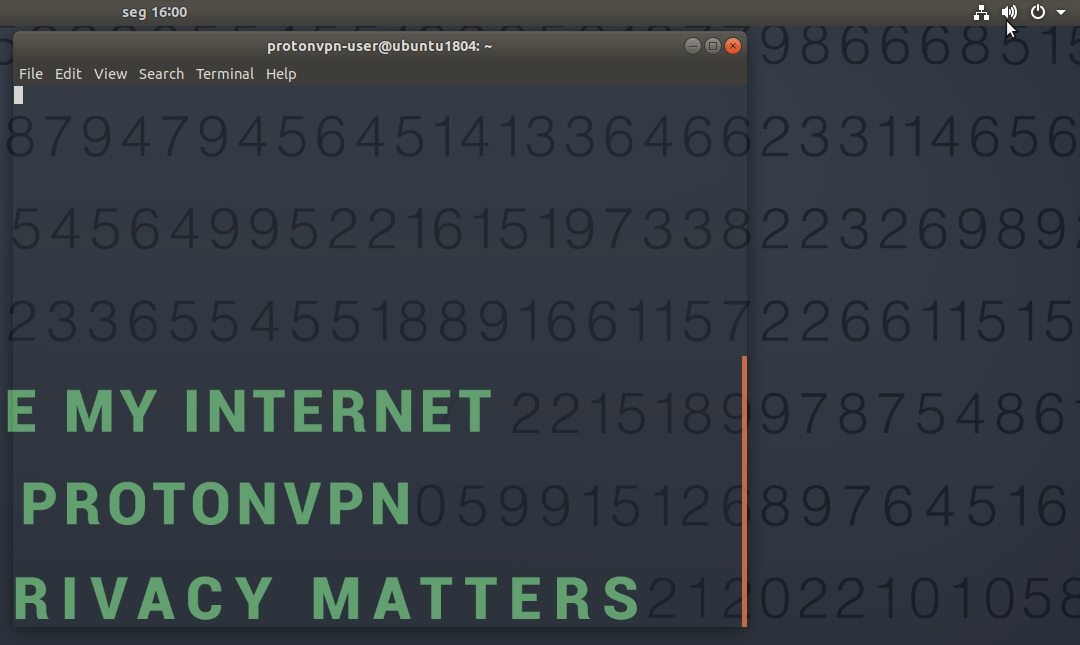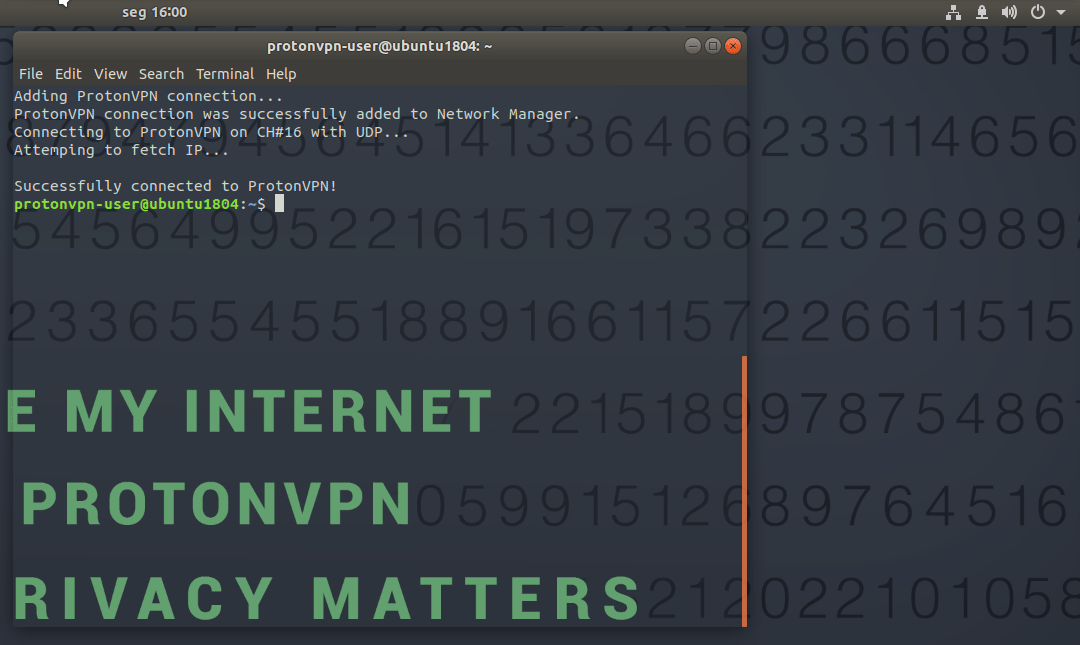 A connection to the VPN server will now be established. To check your connection status, enter:
A connection to the VPN server will now be established. To check your connection status, enter:
protonvpn-cli status (or protonvpn-cli s)
To disconnect, enter:
protonvpn-cli disconnect (or protonvpn-cli d)
Alternatively, you can disconnect using NetworkManager.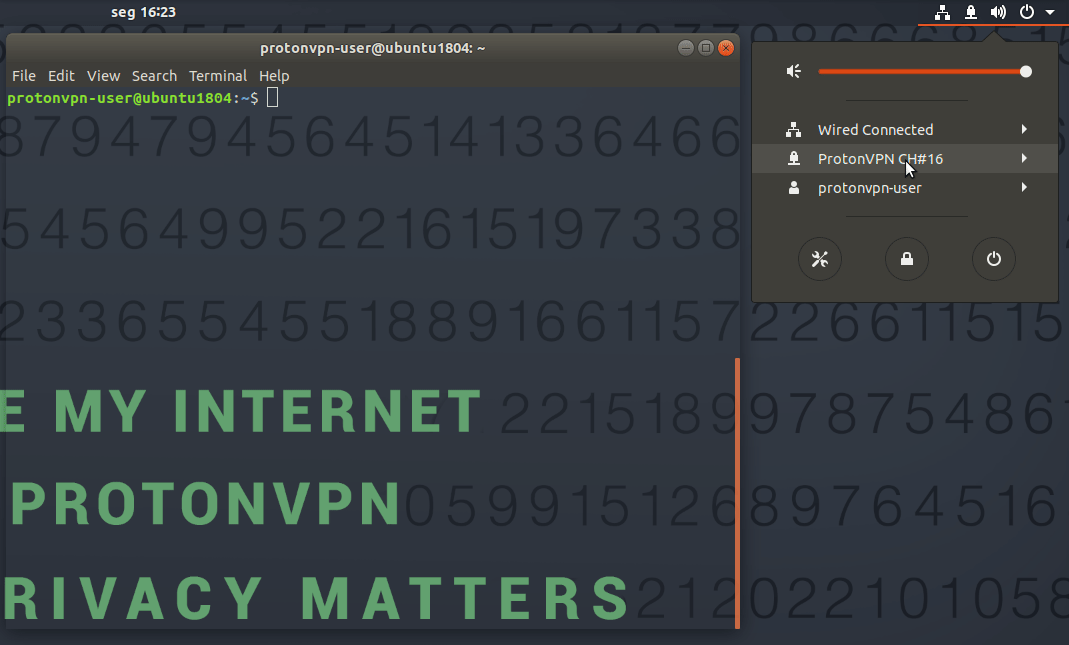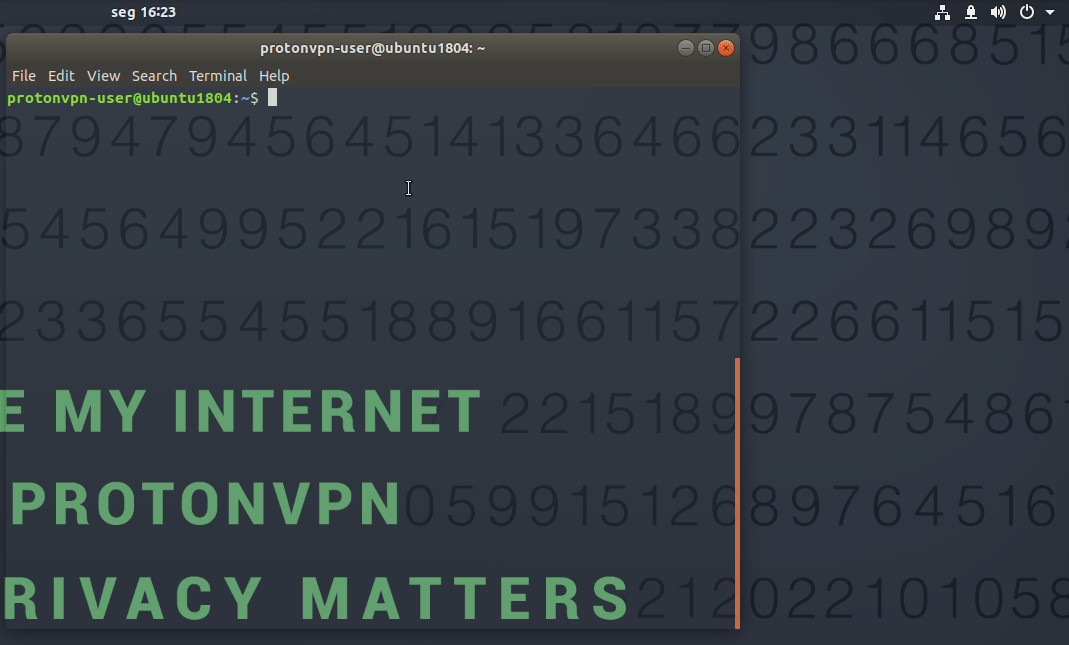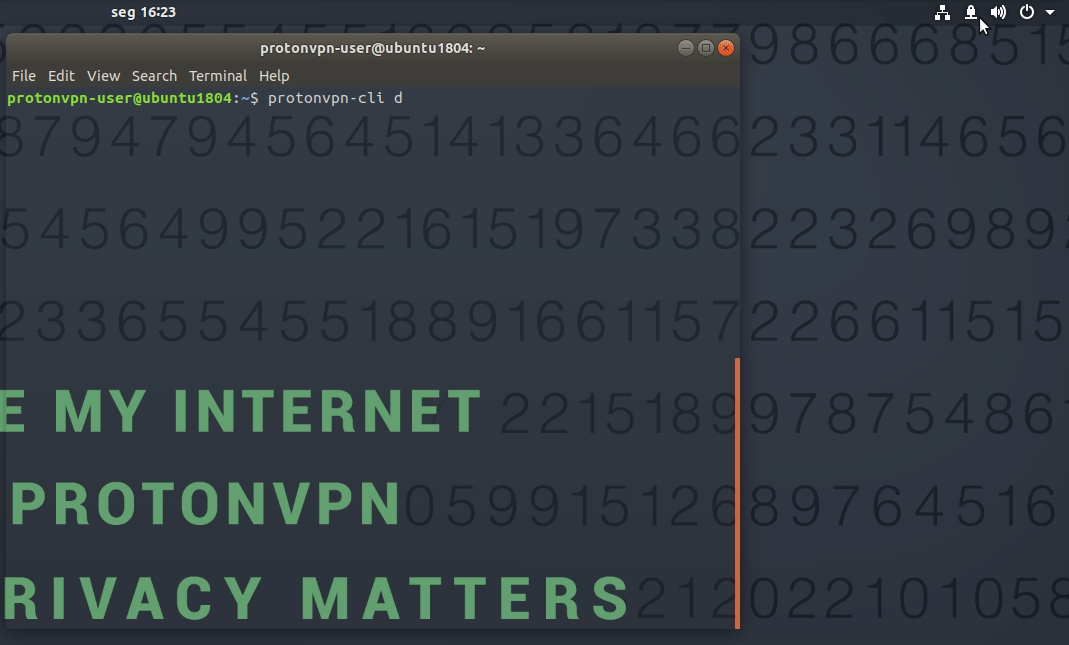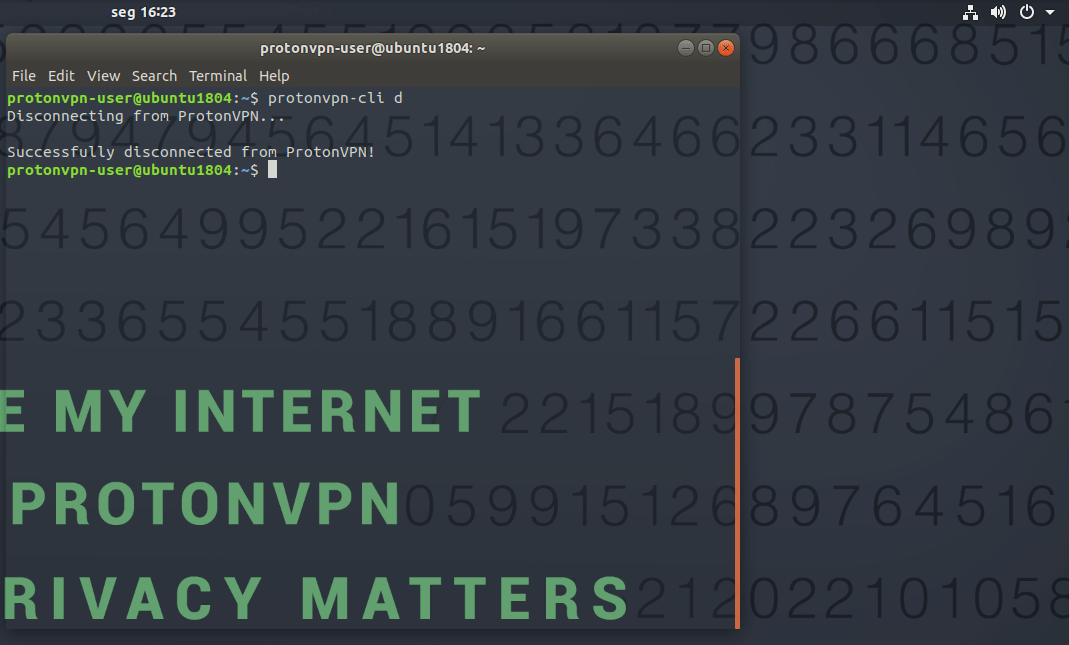
How to use the kill switch
The ProtonVPN official Linux app includes a kill switch. The basic kill switch will block all your internet connections when the VPN app is running and the connection to one of our servers fails. To enable it, enter:
protonvpn-cli ks --onThe app also features an always-on kill switch. This prevents all internet connections unless the VPN app is running and connected to one of our servers. To enable it, enter:
protonvpn-cli ks --always-onYou can disable the kill switch by entering:
protonvpn-cli ks --offHow to connect using the command-line
To see the full list of connection options, enter:
protonvpn-cli c --help  To connect to the fastest ProtonVPN server for your location, for example, enter:
To connect to the fastest ProtonVPN server for your location, for example, enter:
protonvpn-cli c -fOr to connect to the fastest Tor server (Plus and Visionary users only), enter:
protonvpn-cli c --torAdditional connection options, including specifying a custom DNS server, can be found by entering:
protonvpn-cli config --helpPlease note that the official Linux app beta is under active development, so there may be changes to the commands described above. Entering protonvpn-cli h (or protonvpn-cli –help) will always show the latest commands supported by the app.
How to uninstall the official Linux CLI app
If you wish to uninstall the ProtonVPN official Linux CLI app, open Terminal and disable the kill switch (if it is running). To do this, enter:
protonvpn-cli ks --offThen:
Debian distros
1. Uninstall the app with:
sudo apt-get autoremove protonvpn3. Remove any leftover files:
rm -rf ~/.cache/protonvpnAnd
rm -rf ~/.config/protonvpnFedora 33
1. Uninstall the app with:
sudo dnf remove protonvpn -y; sudo dnf autoremove -y; sudo dnf clean packages
2. Check if all ProtonVPN packages are uninstalled:
dnf/yum list installed | grep proton
3. Check if any ProtonVPN folders remain on your system:
ls -ld /usr/lib/python3.*/site-packages/proton*
If any folders are found then remove them using:
sudo rm -rf /usr/lib/python3.*/site-packages/proton*
4. Check again that all folders are removed (see Step 3 above).
Notes
1. Uninstall the older community ProtonVPN app
To uninstall the older community ProtonVPN app, run:
protonvpn configure
Select option 7) Purge Configuration. Then uninstall through the package manager you used for installation. For Debian, if the package is installed system-wide then use the command:
sudo pip3 uninstall protonvpn-cli
If not, then use:
pip3 uninstall protonvpn-cli
2. Add the add-apt-repository command
Some minimal Debian distros (for example, Knoppix) do not include the add-apt-repository command. If you are missing this command then you can install it by running:
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
3. Disable the kill switch if you have uninstalled the app
The kill switch can be easily disabled from within the official Linux app, but this will not be possible if you have uninstalled the app first without disabling the kill switch. This may result in your system being unable to access the internet. To remove the kill switch after the app has been uninstalled:
a) Identify ProtonVPN connection names by running the command:
nmcli connection show --active
This will display a list of all your system’s active connections.
b) Look for any connections with the pvpn- prefix. This usually includes pvpn-killswitch and pvpn-ipv6leak-protection, and may include pvpn-routed-killswitch. Delete all these connections using the following command:
nmcli connection delete [connection name]
For example:
nmcli connection delete pvpn-killswitch
c) Re-run the following command to verify that ProtonVPN connections have been deleted:
nmcli connection show --active
If any ProtonVPN connections remain, delete them as described above.
4. Required dependencies
Comments
Post a Comment